Prefabricated Homes: Features, Costs, And Benefits In 2025
Prefabricated homes, also known as prefab or modular homes, represent an evolving approach to housing construction. Unlike traditional homes built entirely on-site, prefabricated homes are manufactured in sections within controlled factory environments and then transported to the final location for assembly. As we move into 2025, these innovative housing solutions continue to gain popularity across the United Kingdom due to their efficiency, sustainability features, and adaptability to modern living requirements. This comprehensive guide explores the essential features, cost considerations, and benefits that prefabricated homes offer in the current housing landscape.
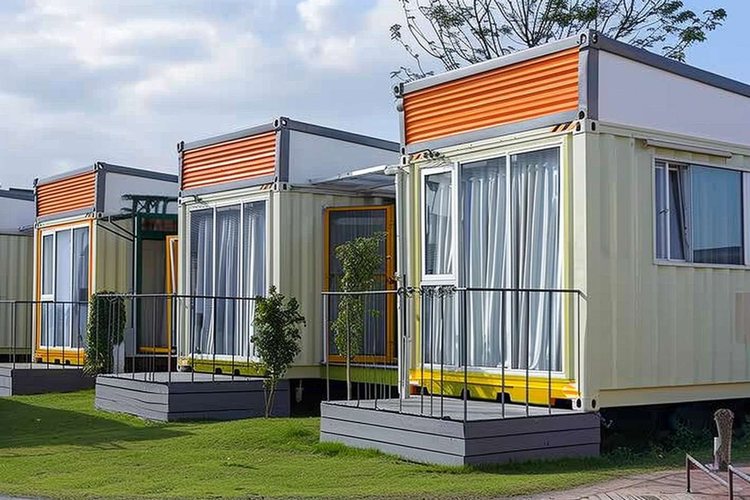

Essential Features Of Prefabricated Homes
Prefabricated homes in 2025 incorporate numerous innovative features that distinguish them from their predecessors. Modern prefab designs utilize advanced building materials that enhance energy efficiency while maintaining structural integrity. Most current prefab homes feature high-performance insulation systems that significantly reduce heat loss during colder months. Factory-controlled production ensures precise measurements and tight seals around windows and doors, minimizing air leakage common in traditional construction.
Many prefabricated homes now incorporate smart home technology as standard features, with integrated systems for climate control, security, and energy management. These homes typically arrive with pre-installed wiring for high-speed internet connectivity and automated home systems. Structurally, prefabricated homes employ engineered wood products and reinforced frames that often exceed building code requirements, providing excellent resistance to environmental stressors like high winds and seismic activity.
Customization options have expanded considerably, with manufacturers offering various floor plans, exterior finishes, and interior design choices. Homeowners can select from traditional styles that blend with existing neighbourhoods or more contemporary designs featuring open floor plans and large windows for natural light. Additionally, many prefabricated homes now incorporate sustainable features such as solar panel integration, rainwater collection systems, and energy-efficient appliances.
Cost Comparison Of Different Prefabricated Home Options
The financial considerations of prefabricated homes vary significantly depending on the type, size, and customization level. Entry-level modular homes typically range from £1,200 to £1,800 per square metre in the UK market, while higher-end prefabricated options with premium finishes and advanced features may cost between £2,000 and £3,000 per square metre. These figures represent the base structure cost, with additional expenses for land, foundation work, utility connections, and final finishing.
Container homes, which utilize repurposed shipping containers, offer a more economical option at approximately £900 to £1,500 per square metre but may have limitations regarding space and customization. Timber-framed prefab homes, popular for their aesthetic appeal and environmental benefits, typically fall in the £1,500 to £2,200 per square metre range. Structurally insulated panel (SIP) homes, known for superior energy efficiency, generally cost between £1,400 and £2,100 per square metre.
| Prefab Home Type | Size Range | Base Cost Range (£) | Energy Efficiency | Construction Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modular Homes | 70-200 m² | £84,000-£360,000 | High | 3-4 months |
| Container Homes | 30-100 m² | £27,000-£150,000 | Medium | 2-3 months |
| Timber Frame | 80-250 m² | £120,000-£550,000 | Very High | 4-5 months |
| SIP Construction | 60-180 m² | £84,000-£378,000 | Excellent | 3-4 months |
| Luxury Prefab | 100-300 m² | £200,000-£900,000 | High | 5-6 months |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
While the initial construction costs often compare favorably to traditional building methods, additional savings emerge through shorter construction timelines, reducing financing costs and temporary housing expenses. Most prefabricated home manufacturers offer financing options similar to conventional mortgages, though some lenders may require specialized loan products for modular construction. Insurance costs typically align with traditional homes of similar size and value, though this varies by provider and location.
Benefits Of Prefabricated Homes
The advantages of choosing prefabricated housing in 2025 extend beyond mere cost-efficiency. Construction speed represents one of the most significant benefits, with typical prefab homes requiring 50-60% less time to complete compared to traditional construction. This accelerated timeline reduces vulnerability to weather delays and minimizes disruption to surrounding properties and communities.
Environmental benefits remain a compelling advantage as prefabricated construction generates approximately 30-40% less waste than conventional building methods. Factory-controlled assembly allows for precise material ordering and efficient recycling of excess components. Many prefab manufacturers now utilize sustainable building materials, including recycled steel, responsibly sourced timber, and low-VOC finishes that improve indoor air quality. The energy efficiency of these homes translates to reduced operational costs, with some high-performance prefab designs achieving near-passive house standards that significantly lower heating and cooling requirements.
Quality control represents another significant benefit of factory-based construction. Each component undergoes rigorous inspection before leaving the production facility, reducing defects commonly found in on-site construction. Modern prefabricated homes demonstrate remarkable durability, with many manufacturers offering structural warranties exceeding those of traditional homes. Additionally, the precision engineering of prefabricated components often results in tighter building envelopes and better overall performance in terms of air infiltration and moisture management.
The flexibility of prefabricated design proves particularly valuable for challenging building sites or locations with limited construction access. Components can be transported to remote areas where traditional construction would pose logistical difficulties. Many prefabricated systems also allow for future expansion or reconfiguration as family needs change, providing adaptability not easily achieved with conventional construction methods.
Future Trends In Prefabricated Housing For 2025
As we progress through 2025, several emerging trends are reshaping the prefabricated housing market. Advanced manufacturing technologies, including 3D printing and robotics, are being integrated into production processes, improving precision while reducing labor costs. Biophilic design principles are increasingly incorporated into prefabricated home designs, with features such as living walls, integrated planters, and natural material selection enhancing connections to the outdoor environment.
Modular prefabricated systems continue to evolve toward greater flexibility, allowing homeowners to start with smaller footprints and expand incrementally as needs and budgets permit. This scalability makes prefabricated homes particularly attractive to first-time buyers and those seeking to minimize initial investment while maintaining future growth options. Additionally, prefabricated components are increasingly being utilized in hybrid construction approaches, combining the efficiency of factory production with site-built elements to optimize both quality and customization.
The prefabricated housing sector continues to mature with improved regulations and standards addressing previous concerns about structural integrity and longevity. As these homes demonstrate their resilience and value retention, financial institutions are developing more specialized lending products tailored to prefabricated construction, further streamlining the purchasing process for prospective homeowners.