Safety and Efficiency Guidelines for Residential Gas Heating
Gas heating systems provide reliable warmth for millions of homes worldwide, but proper safety measures and efficiency practices are essential for optimal performance. Understanding installation requirements, maintenance schedules, and modern safety features helps homeowners make informed decisions while ensuring their family's comfort and security. Regular inspections, proper ventilation, and professional servicing form the foundation of safe gas heating operation.
Gas heating systems remain one of the most popular choices for residential heating due to their reliability, cost-effectiveness, and instant heat delivery. Modern gas heating technology has evolved significantly, incorporating advanced safety features and improved efficiency ratings that benefit both homeowners and the environment.
Choosing the Best Gas Heating for Your Home
Selecting an appropriate gas heating system requires careful consideration of your home’s size, layout, and specific heating needs. High-efficiency condensing boilers typically achieve 90-95% efficiency ratings, while conventional systems operate at 70-80% efficiency. Factors such as available gas supply, existing ductwork, and local climate conditions influence the optimal choice. Modulating gas furnaces adjust their output based on heating demand, providing consistent temperatures while reducing energy consumption. Zoned heating systems allow independent temperature control for different areas, maximizing comfort and efficiency.
Gas Heating 2025: Safety Checks to Prioritize
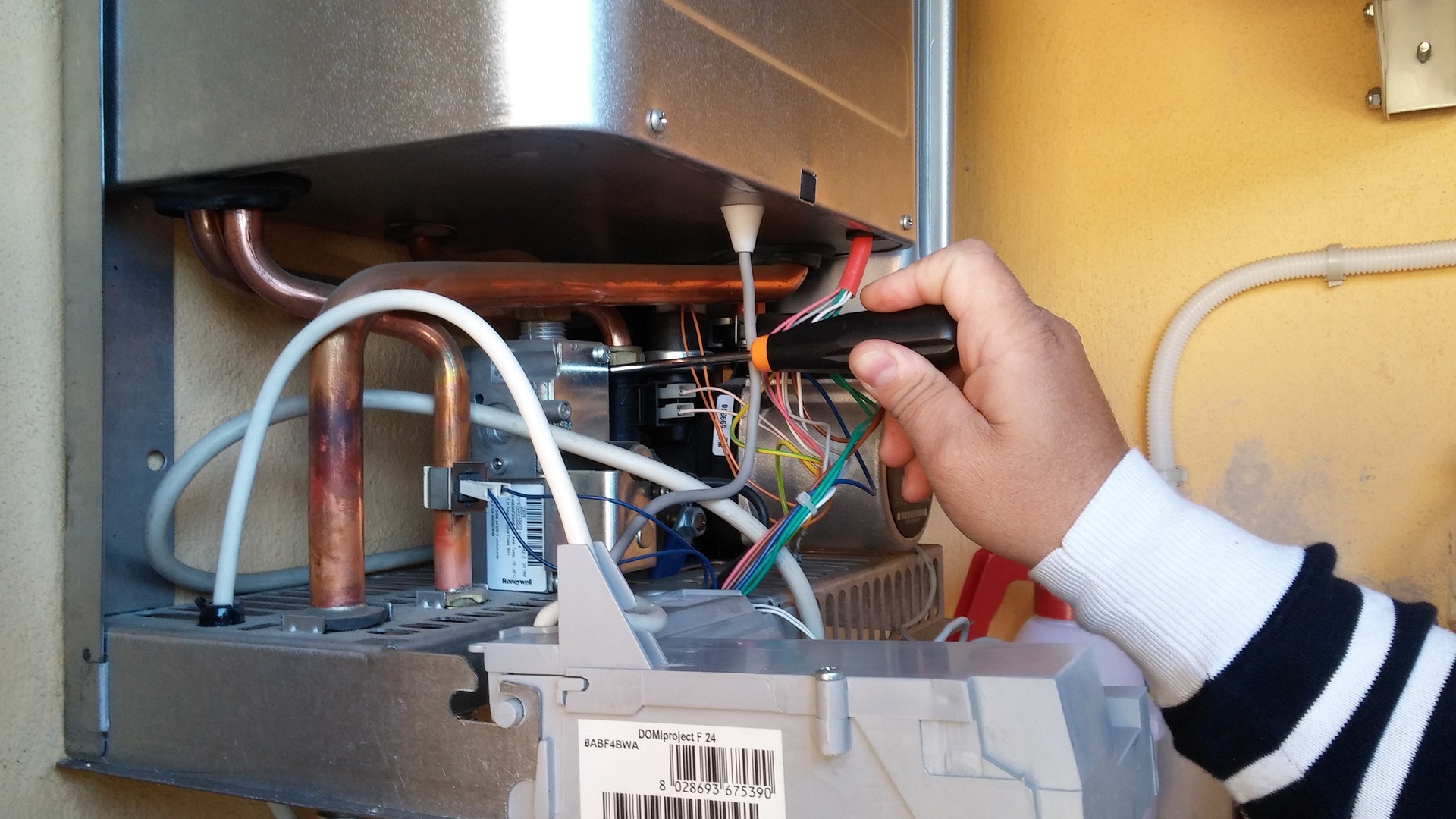
Regular safety inspections are crucial for preventing gas leaks, carbon monoxide poisoning, and system malfunctions. Annual professional inspections should include checking gas connections, testing safety shutoff valves, and examining heat exchangers for cracks or corrosion. Carbon monoxide detectors must be installed near sleeping areas and tested monthly. Gas line pressure testing ensures proper fuel delivery and identifies potential leak points. Flue gas analysis confirms complete combustion and proper ventilation. Homeowners should recognize warning signs such as yellow flames, unusual odors, or excessive moisture around the unit.
Efficient Gas Heating Solutions and Home Habits
Maximizing heating efficiency involves both equipment optimization and behavioral adjustments. Programmable thermostats can reduce energy consumption by 10-15% through automatic temperature scheduling. Proper insulation and air sealing prevent heat loss, allowing heating systems to operate more efficiently. Regular filter replacement maintains airflow and system performance. Closing vents in unused rooms redirects heated air to occupied spaces. Setting thermostats to 68°F during occupied hours and reducing temperatures when away or sleeping significantly impacts energy bills. Smart thermostats learn household patterns and automatically adjust settings for optimal efficiency.
Professional Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Gas heating installation requires licensed technicians who understand local codes, safety regulations, and proper sizing calculations. Improper installation can lead to safety hazards, reduced efficiency, and voided warranties. Professional installation includes gas line sizing, venting requirements, electrical connections, and system commissioning. Annual maintenance services typically include cleaning burners, checking safety controls, lubricating moving parts, and testing system operation. Maintenance contracts often provide priority service, discounted repairs, and extended warranties.
| Service Type | Provider Examples | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|
| Annual Maintenance | Local HVAC Companies | $150-$300 |
| System Installation | Carrier, Trane, Lennox Dealers | $3,000-$8,000 |
| Emergency Repairs | 24/7 Service Companies | $200-$500 |
| Safety Inspections | Certified Gas Technicians | $100-$200 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Environmental Considerations and Future Trends
Modern gas heating systems produce fewer emissions than older models, with high-efficiency units reducing carbon footprints significantly. Condensing technology recovers heat from exhaust gases, improving efficiency while reducing waste. Future trends include hybrid systems combining gas heating with electric heat pumps, providing flexibility and efficiency optimization based on outdoor temperatures. Smart home integration allows remote monitoring and control, enabling predictive maintenance and energy optimization. Renewable natural gas and hydrogen blending represent emerging technologies that may reduce environmental impact while maintaining system compatibility.
Proper gas heating safety and efficiency require ongoing attention to installation quality, regular maintenance, and responsible operation practices. Homeowners who invest in professional services, modern equipment, and energy-efficient habits enjoy reliable comfort while minimizing safety risks and operating costs. Understanding these guidelines helps ensure gas heating systems provide safe, efficient warmth for years to come.