Top Heaters for Winter 2025: Key Factors and Options to Consider
As temperatures drop and winter approaches, finding the right heating solution becomes essential for maintaining comfort in your home. With numerous heating technologies available on the market, understanding the key factors that influence heater performance, efficiency, and suitability for different spaces can help you make an informed decision. This guide explores important considerations when selecting winter heaters, examines various heater types, and provides practical tips for maximizing energy efficiency while keeping your living spaces warm throughout the cold season.
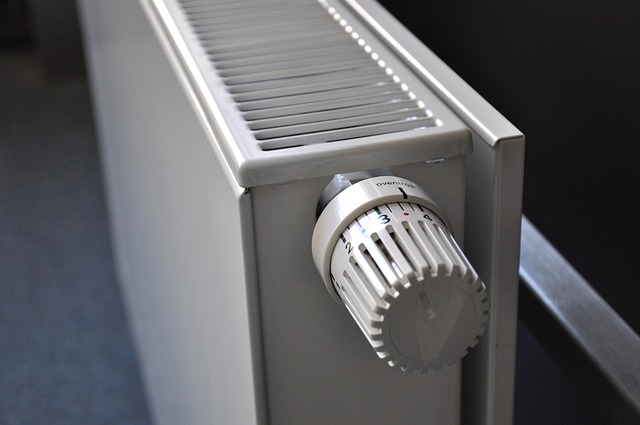

Selecting an appropriate heating solution requires careful consideration of multiple factors that affect both comfort and cost. The size of your space, insulation quality, local climate conditions, and energy costs all play crucial roles in determining which heater type will work best for your specific needs. Understanding these elements before making a purchase can help ensure optimal heating performance and avoid unnecessary expenses.
Key Factors When Selecting Winter Heaters
When evaluating heating options, several critical factors should guide your decision-making process. Room size stands as one of the most important considerations, as heaters are typically rated by the square footage they can effectively warm. A heater too small for your space will run constantly without achieving comfortable temperatures, while an oversized unit may cycle on and off inefficiently. Additionally, consider your home’s insulation quality, ceiling height, and the number of windows, as these factors significantly impact heat retention. Safety features such as tip-over protection, overheat shut-off mechanisms, and cool-touch exteriors are essential, especially in households with children or pets. Portability requirements, noise levels, and installation complexity should also factor into your choice, depending on whether you need a permanent heating solution or a portable option that can move between rooms.
Best Types of Heaters in 2025
The heating market offers several distinct technologies, each with unique advantages suited to different applications. Convection heaters work by warming air that naturally circulates throughout a room, making them ideal for consistent, whole-room heating over extended periods. Radiant heaters emit infrared radiation that directly warms objects and people in their path, providing immediate warmth without heating the entire air volume, which makes them efficient for spot heating. Oil-filled radiators retain heat exceptionally well and continue radiating warmth even after being switched off, offering silent operation and steady temperature maintenance. Ceramic heaters use ceramic heating elements that warm quickly and often include fans to distribute heat more rapidly across spaces. Each technology presents trade-offs between heating speed, energy consumption, noise levels, and suitability for different room sizes and usage patterns.
Comparison of Common Heater Types and Cost Considerations
Understanding the typical price ranges and operational characteristics of different heater types helps in making budget-conscious decisions. The following comparison provides general cost estimations based on current market conditions:
| Heater Type | Typical Price Range | Key Features | Estimated Monthly Operating Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ceramic Fan Heater | $25 - $80 | Quick heating, portable, compact | $30 - $50 (8 hours daily use) |
| Oil-Filled Radiator | $50 - $150 | Silent operation, heat retention | $35 - $55 (8 hours daily use) |
| Infrared Radiant Heater | $40 - $200 | Instant warmth, zone heating | $25 - $45 (8 hours daily use) |
| Convection Heater | $30 - $120 | Whole-room heating, even distribution | $40 - $60 (8 hours daily use) |
| Micathermic Panel Heater | $80 - $250 | Combination heating, slim profile | $30 - $50 (8 hours daily use) |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Operating costs depend heavily on local electricity rates, heater wattage, usage duration, and thermostat settings. These estimates assume average electricity costs and moderate climate conditions.
Tips for Energy-Efficient Heating
Maximizing heating efficiency not only reduces energy bills but also minimizes environmental impact. Start by using programmable thermostats or built-in timers to heat spaces only when occupied, avoiding energy waste during sleeping hours or when away from home. Maintaining temperatures around 68-70°F (20-21°C) during waking hours and lowering them at night can significantly reduce consumption without sacrificing comfort. Proper insulation and weatherstripping around doors and windows prevent heat loss, allowing your heater to work less intensively. Using heaters with adjustable thermostats rather than fixed-output models enables better temperature control and prevents overheating. Zone heating strategies, where you heat only occupied rooms rather than the entire home, can dramatically cut energy usage, particularly in larger residences. Regular maintenance, including cleaning dust from heating elements and ensuring proper airflow, maintains optimal efficiency. Additionally, combining heaters with ceiling fans set to reverse (clockwise) helps circulate warm air that naturally rises, distributing heat more evenly throughout rooms.
Choosing the Right Heater for Your Home
Matching heater characteristics to your specific living situation ensures both comfort and cost-effectiveness. For small personal spaces like home offices or bedrooms, compact ceramic or fan heaters provide quick, targeted warmth with minimal investment. Medium-sized living areas benefit from oil-filled radiators or convection heaters that deliver consistent, even heating without constant noise. Large open-plan spaces may require multiple heating units or higher-wattage models capable of warming greater volumes efficiently. Homes with good insulation can achieve comfort with lower-wattage heaters, while poorly insulated spaces may need more powerful options or supplementary heating sources. Consider your climate zone as well—mild winter regions may only need occasional supplemental heating, while areas with harsh winters require reliable, high-capacity heating solutions. Budget constraints naturally influence choices, but remember that energy-efficient models, despite higher upfront costs, often provide better long-term value through reduced operating expenses. Finally, evaluate your lifestyle needs: families with young children should prioritize safety features, while those seeking minimal maintenance might prefer sealed oil-filled units over models requiring filter cleaning.
Selecting the right winter heating solution involves balancing multiple considerations including space requirements, budget constraints, energy efficiency goals, and personal comfort preferences. By understanding the strengths and limitations of different heater types and implementing energy-saving practices, you can create a warm, comfortable home environment while managing heating costs effectively throughout the winter season.